Browsing: Trauma
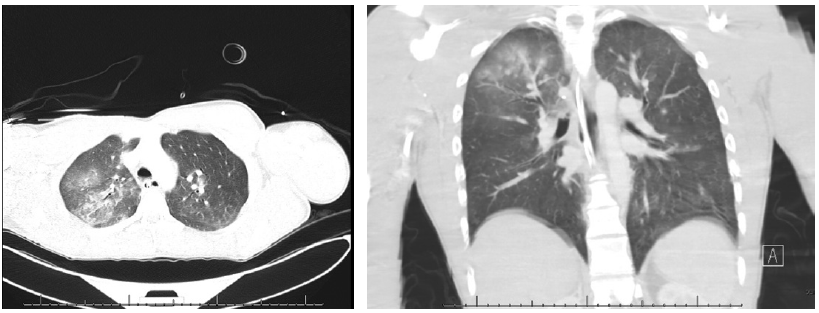

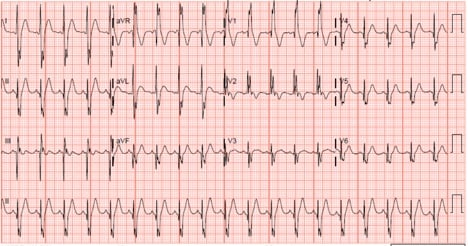
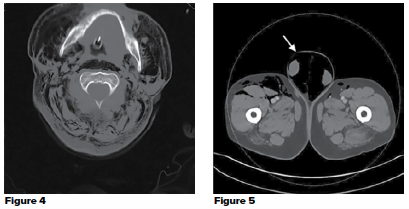
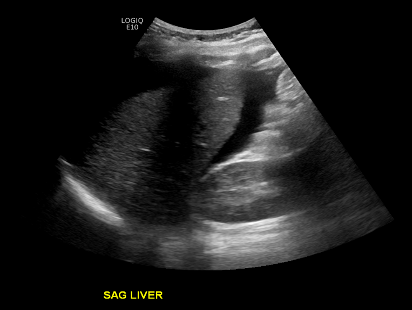
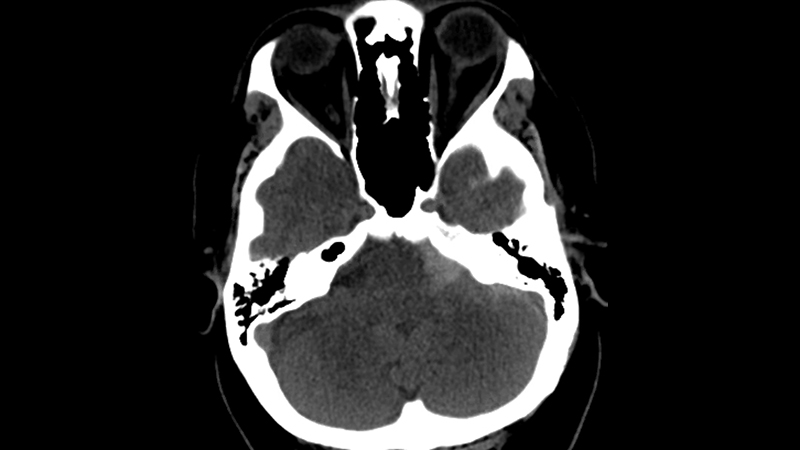


Investigate the pressure of this tangled case of a patient with a limb-threatening injury at first discharged home in the absence of a fracture.


