Browsing: Cardiology



Critical Care
,
Critical Care Alert
,
Cardiology
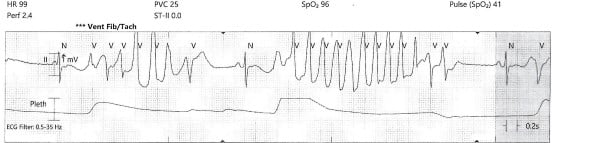
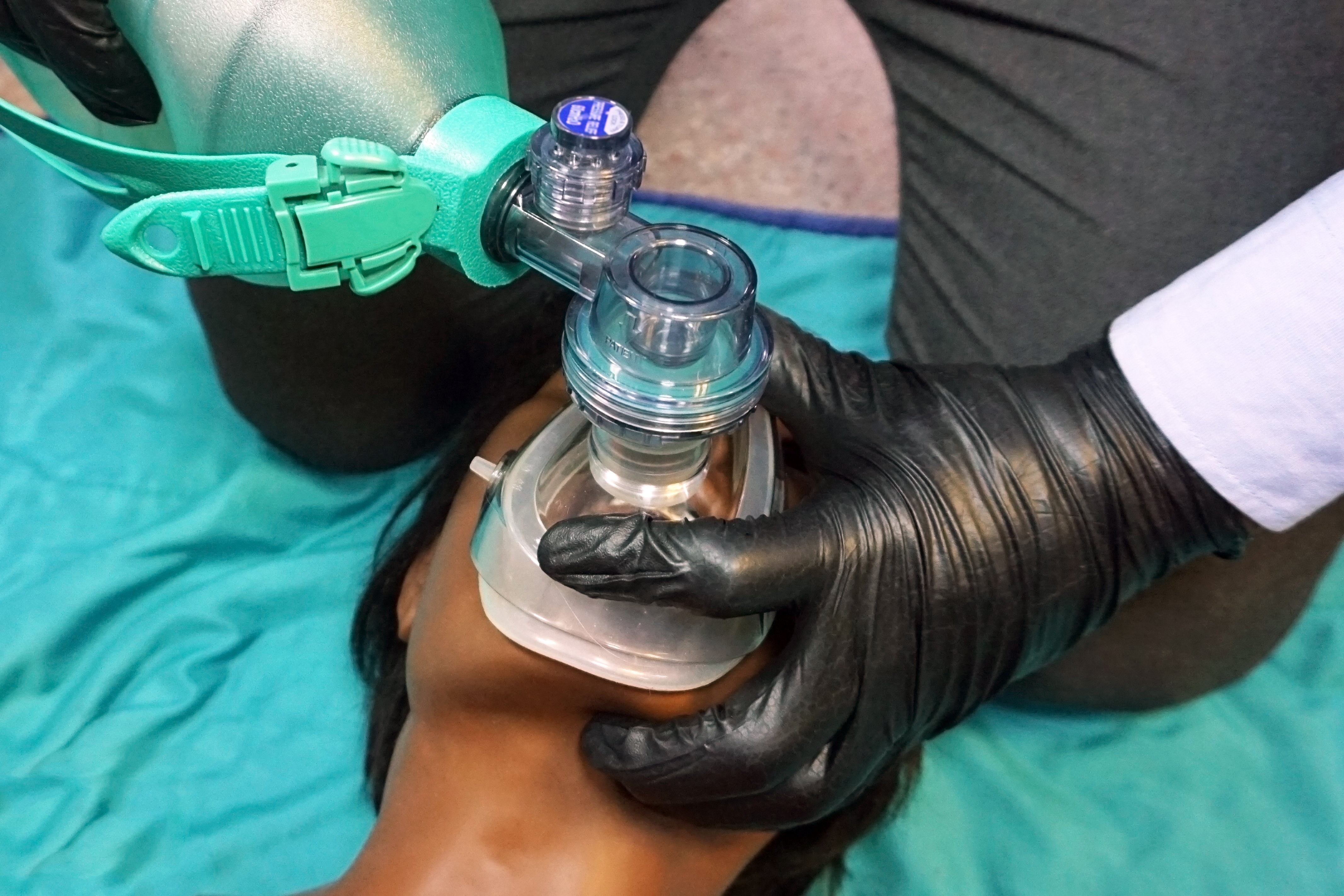
The evidence surrounding ECPR continues to build. In this study, investigators demonstrated a 31.5% survival rate with favorable 180-day neurological outcome with ECPR in patients who suffered out-of-
Critical Care Alert: Effect of Intra-arrest Transport, Extracorporeal Cardiopulmonary Resuscitation, and Immediate Invasive Assessment and Treatment on Functional Neurologic Outcome in Refractory Out-of-Hospital Cardiac Arrest
5/14/2022 Erin Bell, MD , Taylor Miller, MD