Browsing: Topics






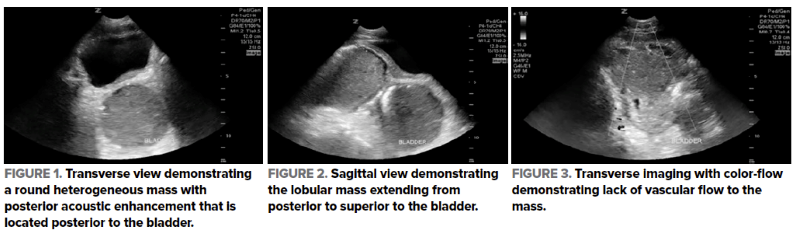

Administration & Operations
,
Health Care Administration
,
Medical Education
Emergency medicine (EM) residency exposes trainees to the informal curriculum of practice management. Through the Kern model of curriculum development, we present a national targeted needs assessment


