Browsing: Critical Care

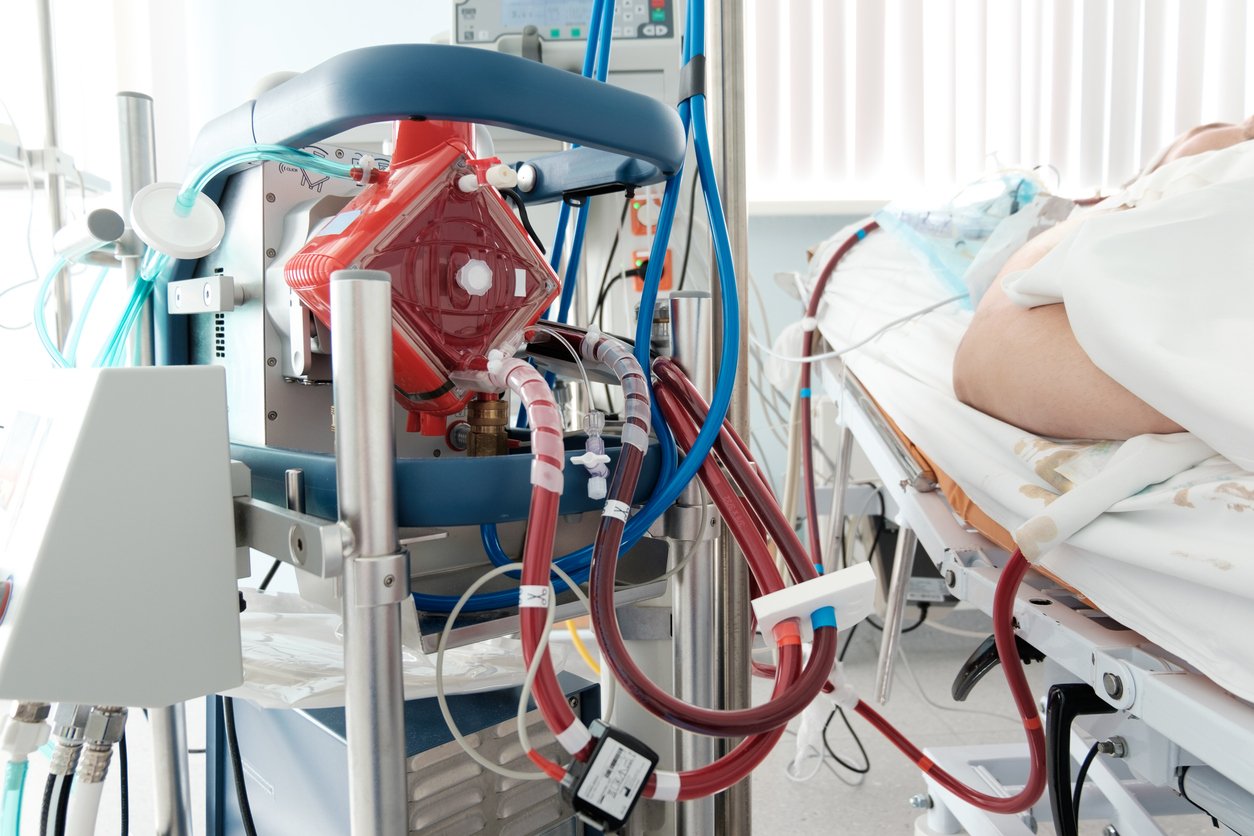
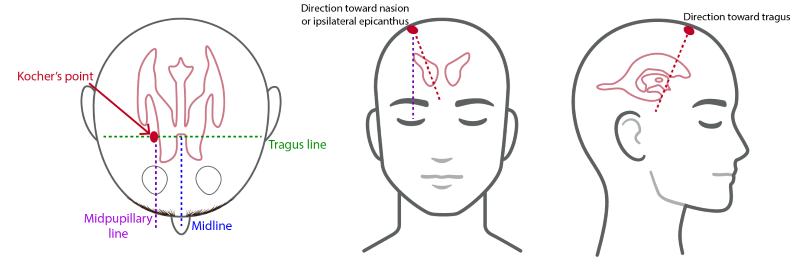
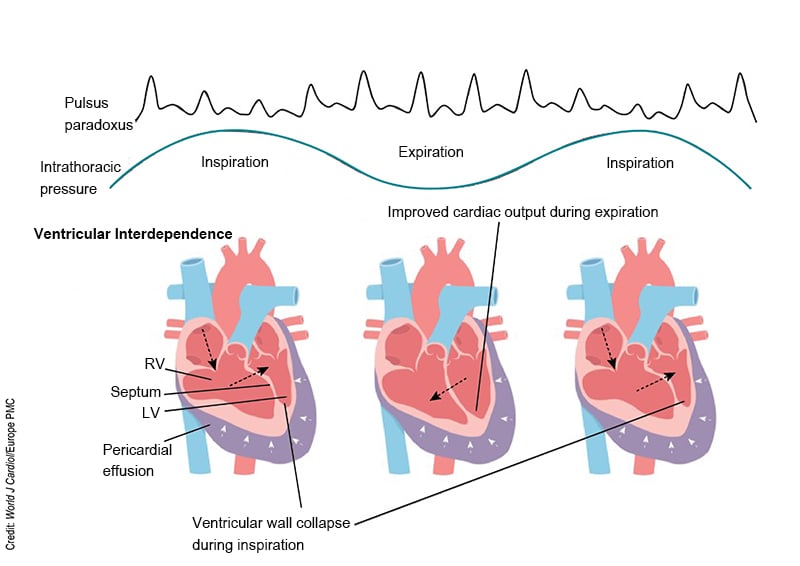
Deep Dive in CritCare
,
Critical Care
,
Neurology
Elevated ICP is an emergent complication associated with injury to the brain. In this Deep Dive, we summarize the existing evidence regarding the monitoring and management of elevated intracranial pre
Deep Dive into the Evidence: Monitoring and Management of Elevated Intracranial Pressure in Severe Traumatic Brain Injury
6/11/2024 Luxi Qiao, MD, MPhil , Josh Wild, DO , Eleni McCaffery, MD , Dominique Gelmann, MD , Dustin Slagle, MD , Sung-Min Cho, DO, MHS