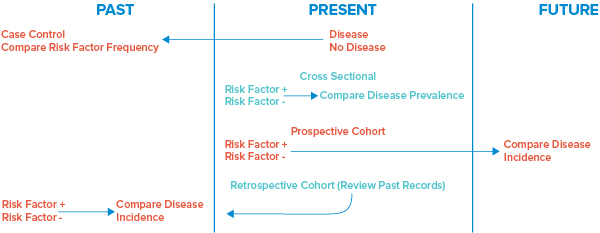
Case-Control (“What happened?”)
Compares a group with a disease to a group without disease. This study can calculate an odds ratio.
Advantages: many exposures can be studied and is useful for rare disorders.
Disadvantages: confounding factors and the potential for recall/selection bias.
Cohort (“What will happen?”)
Compares a group with an exposure/risk factor to a group without exposure. This study can calculate a relative risk.
Advantages: ethically safe, timing and directionality of events can be established
Disadvantages: blinding is difficult; no randomization; controls may be difficult to identify
Cross-Sectional Study (“What is happening?”)
Collects data from a group of people to assess frequency of disease and related risk factors at a particular point in time. This study can help calculate disease prevalence.
Advantages: ethically safe
Disadvantages: potential recall or Neyman bias; association can be established but not causality